New Jersey Tiered Systems of Support
Effectively implementing the New Jersey Tiered System of Supports (NJTSS) to Support Student Learning Gaps
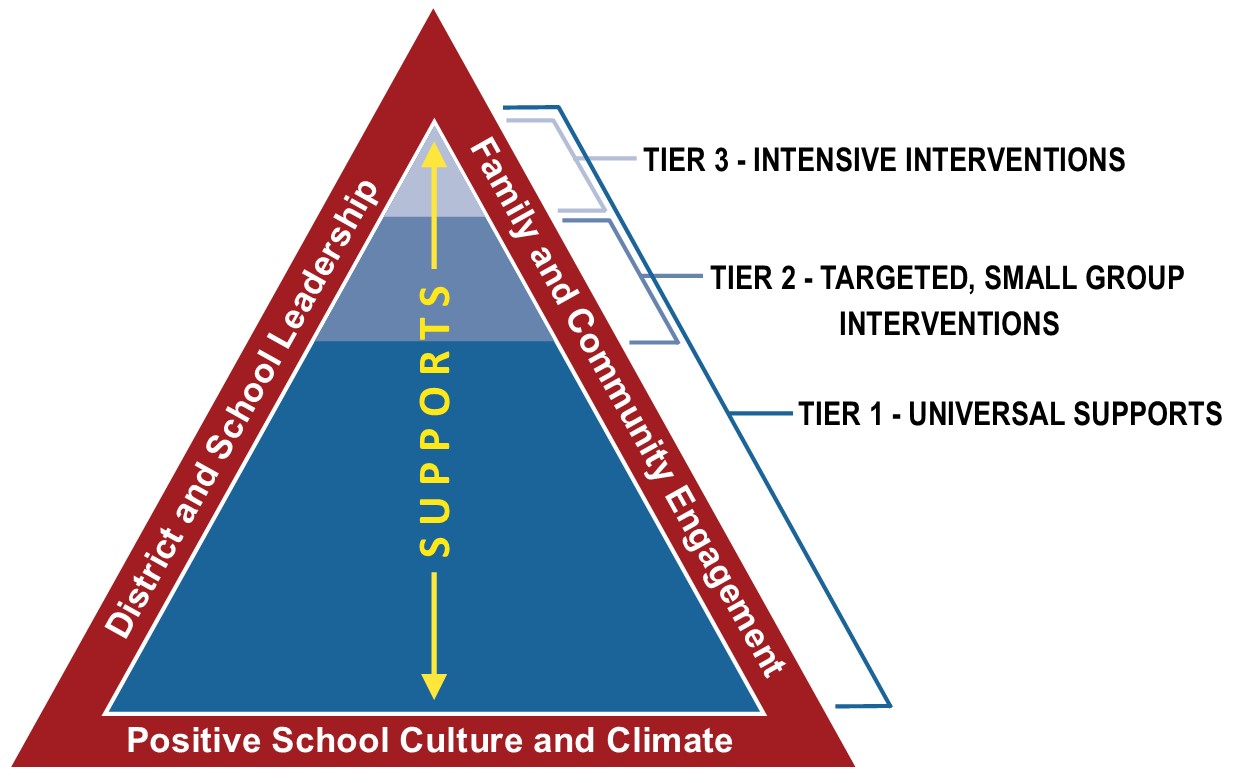 The New Jersey Tiered System of Supports (NJTSS) is a framework of multi-tiered academic and behavioral supports designed to promote student achievement and success and response to intervention (RTI). The NJTSS framework provides schools with a structure for meeting the academic, behavioral, health, enrichment, and social and emotional needs of all students and aligns resources to provide the right interventions to the right students at the right times.
The New Jersey Tiered System of Supports (NJTSS) is a framework of multi-tiered academic and behavioral supports designed to promote student achievement and success and response to intervention (RTI). The NJTSS framework provides schools with a structure for meeting the academic, behavioral, health, enrichment, and social and emotional needs of all students and aligns resources to provide the right interventions to the right students at the right times.
The NJTSS framework includes nine essential components:
Three Foundational Components, around the outer triangle of the diagram:
- Effective district and school leadership
- Family and community engagement
- Positive school culture and climate
Six Instructional Components to support a continuum of core programs and interventions, as in many RTI models:
- High-quality learning environments, curricula, and instructional practices
- Universal screening
- Data-based decision making
- Collaborative problem-solving teams
- Progress monitoring
- Staff professional development
These are included in the three tiers of the diagram’s inner triangle and, depending on the level of intensity required, can be used to address academic, behavioral, social-emotional, and/or health-related needs. Depending on their needs, students may move up or down the tiers or be at different tier levels for different areas of intervention.
Every LEA in New Jersey is required to have some system of intervention and referral service (I&RS) in place, and the NJTSS offers LEAs a useful framework for implementing, expanding, or revising their I&RS process. Building a strong system of supports, however, is an ongoing, iterative effort and one that can be jumpstarted with ESSER funds and sustained with other Federal funding streams.
Key for tables: Y = Yes, likely to be an allowable use of these funds; N = No, unlikely to be an allowable use of these funds
Activities that may be funded
1. Foundational Component: Effective District and School Leadership
- Convene (or reconvene) a district leadership team to determine the status of core programs and intervention systems to address student needs. Ensure that the team has the time and support to meet regularly.
- As a team, review the NJTSS Implementation Guide and work through the “Getting Started with NJTSS” planning tool.
- Administer the revised School Climate Improvement (NJ SCI) survey (or readminister if not conducted recently).
- Review available data from the NJ SCI survey, student performance information, and other data to assess strengths and weaknesses of the LEA’s current system of support.
- Revise policies governing the LEA’s systems of support as needed and ensure there is an ongoing procedure for reviewing these policies.
| ESEA Title I-A | ESEA Title II | ESEA Title III-A | ESEA Title IV-A | McKinney-Vento | Adult Education and Family Literacy Act |
IDEA | Perkins | Early Childhood Programs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | N | N |
2. Foundational Component: Family and Community Engagement
- Inform parents in culturally and linguistically appropriate ways about NJTSS. Ensure that families receive this information at key transition points (elementary to middle school, for example), and that new families receive this information when enrolling their children.
- Make sure school staff appropriately notify parents when their children require additional support and that parents understand how to ask for additional information.
- Build partnerships with community organizations to provide supplemental supports to students in need, including through afterschool, extended day, and summer programs.
- Help families access community supports that may assist with other home-based needs that may be interfering with student learning (such as food or housing insecurity or digital learning access).
- Provide LEA support for the required Special Education Parent Advisory Group (SEPAG), such as through meeting space, recruitment/informational messages, and staff engagement as appropriate.
- Raise expectations of staff in helping families engage with their children’s learning at home, such as by sending regular communications regarding classwork, sharing data, participating in student planning meetings, and providing workshops/parent trainings
| ESEA Title I-A | ESEA Title II | ESEA Title III-A | ESEA Title IV-A | McKinney-Vento | Adult Education and Family Literacy Act |
IDEA | Perkins | Early Childhood Programs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y |
3. Foundational Component: Positive School Culture and Climate
- Work with staff to ensure that the physical school environment is clean, safe, welcoming, accessible, and culturally responsive for all students.
- Help staff have time to understand, build, and implement an effective system of Positive Behavioral Supports in Schools (PBSIS), to ensure there are clearly defined and articulated expectations, transitions, routines, and behavioral interventions for students.
- Train all staff (not just teachers) on culturally responsive practices. Facilitate school and/or LEA team discussions on revising curriculum to be more culturally appropriate.
- Regularly monitor and support staff and student social and emotional health.
- Review LEA and school communication methods and ensure that internal and external communications are effective and welcoming.
- Regularly recognize and celebrate student and staff accomplishments and differences, including cultural, linguistic, and ability differences.
| ESEA Title I-A | ESEA Title II | ESEA Title III-A | ESEA Title IV-A | McKinney-Vento | Adult Education and Family Literacy Act |
IDEA | Perkins | Early Childhood Programs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | N | N |
4. Instructional Component: Universal Screening
- Screen ALL students several times a year to assess academic progress relative to defined benchmarks and identify whether students may require (1) changes to their core instruction, (2) additional intervention, or (3) more challenging instruction. This is particularly critical as schools continue to recover from multiple years of disrupted learning. LEAs can use ESSER funds to develop and implement a screening plan and then sustain it with other Federal funds in the longer term.
- Ensure that teachers have the training necessary to administer screening assessments and interpret the results.
- Ensure that the district complies with N.J.S.A. 18A:40-5.3, which requires districts to ensure that “each student enrolled in the school district who has exhibited one or more potential indicators of dyslexia or other reading disabilities is screened for dyslexia and other reading disabilities using a screening instrument no later than the student’s completion of the first semester of the second grade.”
| ESEA Title I-A | ESEA Title II | ESEA Title III-A | ESEA Title IV-A | McKinney-Vento | Adult Education and Family Literacy Act |
IDEA | Perkins | Early Childhood Programs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | N | N |
5. Instructional Component: High Quality Learning Environments, Curricula, & Instructional Practices
- Use screenings and other assessment measures to regularly move students across support Tiers 1, 2, and 3, as appropriate.
- Develop consistent standards to identify when a student should enter or exit a higher tier of support.
- Work with special education staff to better align referrals and services for students with disabilities. Students with disabilities do not necessarily receive Tier 3 support in every subject and in every setting.
- Ensure all screenings and supports are appropriate for English Language Learners.
| ESEA Title I-A | ESEA Title II | ESEA Title III-A | ESEA Title IV-A | McKinney-Vento | Adult Education and Family Literacy Act |
IDEA | Perkins | Early Childhood Programs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y | N | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | N | Y |
6. Instructional Component: Data-based Decision Making
- Implement a district-wide data management system that includes consistent and comprehensive school-level data accessible to all staff.
- Regularly convene staff teams to analyze aggregate data to identify possible patterns and potential modifications (for example, whether students in a certain ethnic group are more likely to be referred to Tier 3 interventions).
- Provide staff professional development on how to more effectively adapt instructional practices to meet individual student needs.
| ESEA Title I-A | ESEA Title II | ESEA Title III-A | ESEA Title IV-A | McKinney-Vento | Adult Education and Family Literacy Act |
IDEA | Perkins | Early Childhood Programs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | N | Y |
7. Instructional Component: Collaborative Problem-Solving Teams
- Review the LEA’s I&RS process to ensure that it is being implemented effectively, consistently across settings and with different types of students, and as comprehensively as possible.
- Ensure that all relevant staff are involved in the I&RS team and that they meet regularly to review a wide array of data.
| ESEA Title I-A | ESEA Title II | ESEA Title III-A | ESEA Title IV-A | McKinney-Vento | Adult Education and Family Literacy Act |
IDEA | Perkins | Early Childhood Programs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y | N | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | N | Y |
8. Instructional Component: Progress Monitoring
- Review district progress monitoring tools and processes to ensure they are used at the appropriate frequency to make decisions about student progress.
- Work with the I&RS or IEP team to ensure they use data to drive decision-making about student progress and supports.
| ESEA Title I-A | ESEA Title II | ESEA Title III-A | ESEA Title IV-A | McKinney-Vento | Adult Education and Family Literacy Act |
IDEA | Perkins | Early Childhood Programs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y | N | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | N | Y |
9. Instructional Component: Staff Professional Development
- Provide coaching that includes modeling and performance feedback to support the development of high-quality instruction and implementation of interventions with fidelity.
- Support professional learning communities within the LEA, such as at the school or grade level, including by providing time and resources to meet.
- Provide ongoing, job-embedded professional development on understanding data, administering assessments, and any new state or federal requirements guiding assessment and instruction.
| ESEA Title I-A | ESEA Title II | ESEA Title III-A | ESEA Title IV-A | McKinney-Vento | Adult Education and Family Literacy Act |
IDEA | Perkins | Early Childhood Programs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | N |
10. Train all teachers on special education provisions and policies, such as Least Restrictive Requirement (LRE), common accommodations, and manifest determination regulations, to better meet student needs in general education classrooms, wherever possible.
| ESEA Title I-A | ESEA Title II | ESEA Title III-A | ESEA Title IV-A | McKinney-Vento | Adult Education and Family Literacy Act |
IDEA | Perkins | Early Childhood Programs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y | Y | N | N | N | N | Y | N | N |
11. Strengthen collaboration and communication between general education, special education, bilingual/ESL and support teachers to ensure the needs of all students are being met, through opportunities for common planning time or regular sharing of student progress.
| ESEA Title I-A | ESEA Title II | ESEA Title III-A | ESEA Title IV-A | McKinney-Vento | Adult Education and Family Literacy Act |
IDEA | Perkins | Early Childhood Programs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y |
Although this resource discusses Federal laws and regulations, it is intended solely to provide general information and does not constitute legal advice. This guidance provides a general overview of allowable activities, but whether or not a particular cost can be supported with Federal funds depends on the underlying facts and circumstances and State and Federal rules (e.g. New Jersey Treasury Office of Management and Budget (OMB) and Uniform Grant Guidelines, respectively). Therefore, an activity listed in this resource may not be allowable in all circumstances, and conversely, an activity not listed in this resource may be allowable. This guide was created to demonstrate how programs, strategies, or initiatives may be supported with Federal funds. Please note a school or local education agency is under no obligation to use its Federal funds for those programs or activities highlighted in this guide.
 Official Site of The State of New Jersey
Official Site of The State of New Jersey