- Home
- Diseases & Health Topics A-Z List
- Candida auris
Candida auris
Candida auris (or C. auris) is a fungus that is causing serious infections in patients in the United States, including New Jersey. C. auris is primarily found in healthcare settings, particularly in long-term acute care hospitals and nursing homes that take care of patients on ventilators. Patients can carry C. auris on their body, even if it is not making them sick. This is called colonization. When people in hospitals and nursing homes are colonized, C. auris can spread from their bodies and can get on other people or nearby objects, allowing the fungus to spread to people around them. In some patients, this fungus can enter the bloodstream and spread throughout the body, causing serious invasive infections. This fungus often does not respond to commonly used antifungal drugs, making infections difficult to treat.
The New Jersey Department of Health responds to all reports of C. auris in New Jersey and supports prevention efforts through surveillance testing and infection prevention recommendations. If C. auris is suspected or identified, contact your local health department and the NJDOH Communicable Disease Service at (609) 826-5964.
Candida auris Case Definition and Subtypes
Candida auris clinical case: Person with confirmatory laboratory evidence from a clinical specimen collected for the purpose of diagnosing or treating disease in the normal course of care.*
- A clinical case is only counted once, even if the patient later tests positive for C. auris as a screening case. This is because all clinical cases are already considered to be colonized with C. auris. For example, a newly identified clinical C. auris case who subsequently has a positive screening swab would not be also counted as a screening case.
*This includes specimens from sites reflecting invasive infection (e.g., blood, cerebrospinal fluid) and specimens from non-invasive sites such as wounds, urine, and the respiratory tract, where presence of C. auris may simply represent colonization and not true infection. This does not include swabs collected for screening purposes (see Candida auris screening case).
Candida auris screening case: Person with confirmatory laboratory evidence from a swab collected for the purpose of screening for C. auris colonization regardless of site swabbed.**
- For screening cases, patients are counted only once as a screening case; a patient is not counted as a screening case if the patient has been previously identified as a clinical or screening case. A person with a screening case can be later categorized as a clinical case (e.g., patient with positive screening swab who later develops bloodstream infection would be counted in both categories).
**Typical screening specimen sites are skin (e.g., axilla, groin), nares, rectum, or other external body sites. Swabs collected from wound or draining ear as part of clinical care are considered clinical specimens.**
**Because it can be difficult to differentiate screening specimens from clinical specimens based on microbiology records, any swabs except wound swabs or draining ear swabs can be assumed to be for screening unless specifically noted otherwise. Laboratories do not need to change their practice; public health wants to identify all C. auris whether from screening or clinical specimens.
References: https://ndc.services.cdc.gov/case-definitions/candida-auris-2023/
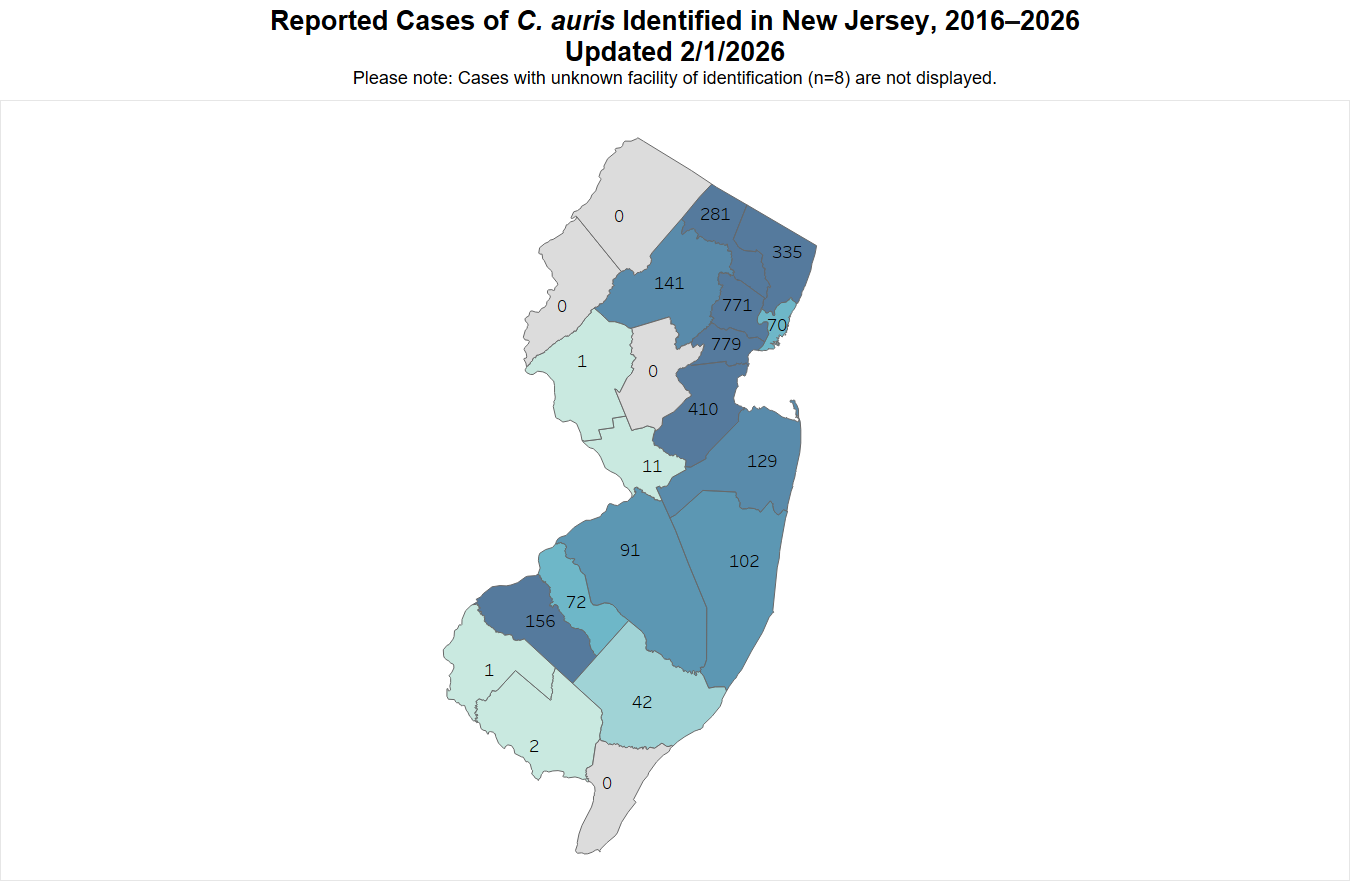
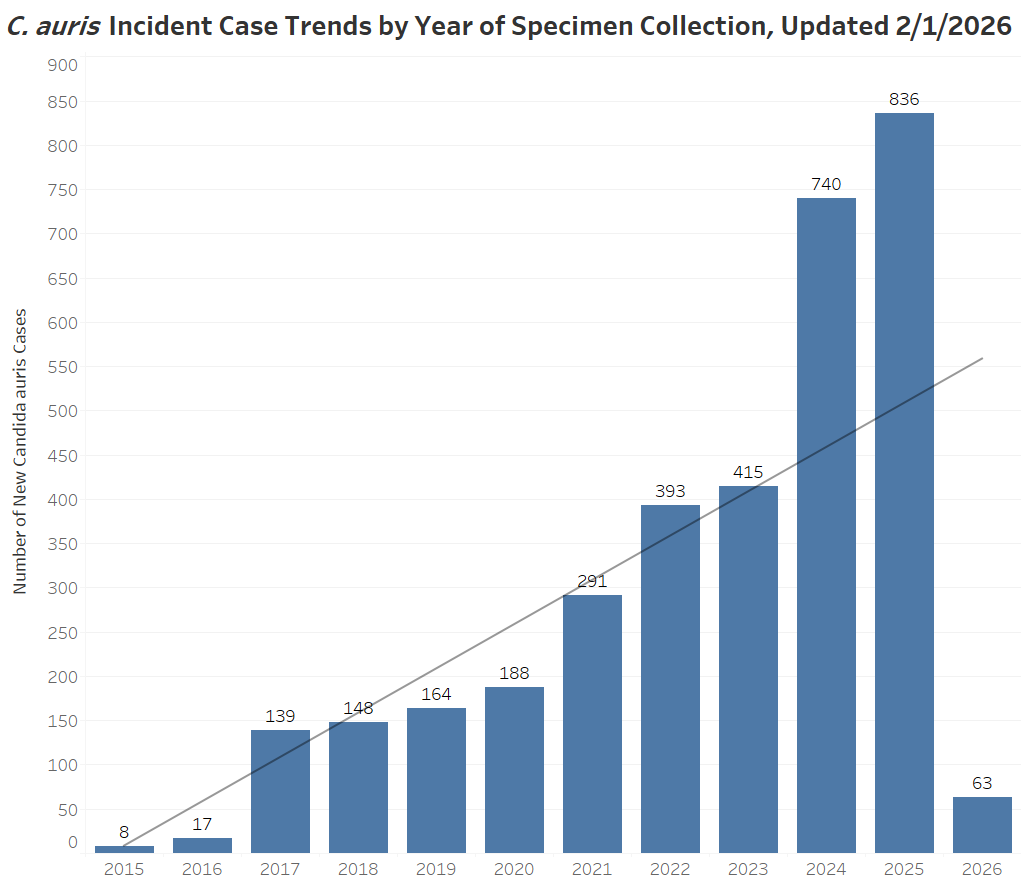
New Jersey Candida auris Case Counts (as of February 1, 2026)
Total Case Count: 3,402
Clinical case count: 754
Screening case count: 2,648
Resources for Patients and Family Members
- Patient Screening FAQs (CDC) [English] [Spanish] [Korean] [Vietnamese]
- Fact Sheet: Information for Patients about Colonization (CDC) [English] [Spanish]
- Fact Sheet: Information for Patients about Testing (CDC) [English] [Spanish]
- Candida auris Patient FAQs (NJDOH)
- Candida auris Patient Discharge Information (NJDOH)
Resources for Laboratorians and Health Professionals
- NEW 6/10/25 Enhanced Barrier Precautions (EBP) in Nursing Homes Algorithm [PDF]
- What is Candida auris? (NJDOH) [Color] [B&W]
- Recommendations for Laboratorians and Health Professionals (CDC)
- Fact Sheet: Information for Infection Preventionist (CDC) [English] [Spanish]
- Fact Sheet: Information for Laboratory Staff (CDC) [English] [Spanish]
- Case Report Form Completion and Submission Instructions (NJDOH)
- Fundamentals of Infection Control for Candida auris positive patients (NJDOH) [Color] [B&W]
- Infection Prevention and Control Guidance for Providing Care to Individuals with Novel MDROs(NJDOH)
- Transmission Based Precautions for Patients with Novel and Targeted MDROs (NJDOH) [Color] [B&W]
- Cleaning and Disinfection against Candida auris (NJDOH) [Color] [B&W]
- Patient Cohorting (NJDOH) [Color] [B&W]
- Infection Prevention and Control for Candida auris (CDC)
- Candida auris Infection Control Actions for Prevention and Response (CDC)
- Prevention of Invasive Candida auris Infections (CDC)
- Screening for Candida auris (CDC)
- Preventing the Spread of Candida auris (CDC)
- Screening for Colonization in Health Care Facilities (CDC)
- Candida auris Screening Patient Swab Collection (CDC)
- Recommendations for Providing Safe Dialysis Care for Patients with Candida auris (NJDOH)
- General Laboratory Considerations and Recommendations for Candida auris Identification. (NJDOH)
- Laboratory Information for Candida auris Identification (CDC)
- Safety Guidelines for Working with Candida auris Isolates (CDC)
- March 24, 2023: Candida auris: Identification, Reporting and Infection Prevention Guidance Updates
- September 13, 2021: Candida auris: Regional Increase in Cases & Testing Guidance
- July 15, 2021: Candida auris: Cleaning and Disinfection Updates and Mandatory Admissions
- June 2020: Potential Multi-drug Resistant Organisms (MDROs) increase during COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) Pandemic
- February 19, 2020: Candida auris in New Jersey
- January 24, 2017: C. auris in New Jersey: Information and Interim Recommendations for Healthcare Facilities and Laboratories
Resources & References
CDC Resources
- CDC Candida auris homepage
- About Candida auris
- Fact Sheet: Candida auris: A Drug-resistant Germ That Spreads in Healthcare Facilities [English][Spanish][Vietnamese] [Korean]
- Clincial Overview of Candida auris (CDC)
- Clinical Care of Candida auris Infections (CDC)
Related NJDOH Links