Delaware • New Jersey • Pennsylvania
New York • United States of America
- Aquatic Life Designated Use Project
- Bacteria Monitoring
- Biomonitoring Program
- Chlorides Monitoring
- Contaminants of Emerging Concern
- Delaware Estuary Water Quality Monitoring Program
- Dissolved Oxygen and Nutrients
- Modeling
- Other Monitoring (e.g., Toxicity, Fish Tissue, Metals)
- PCBs and PMPs
- Special Protection Waters (SPW)
- Water Resource Data Sets
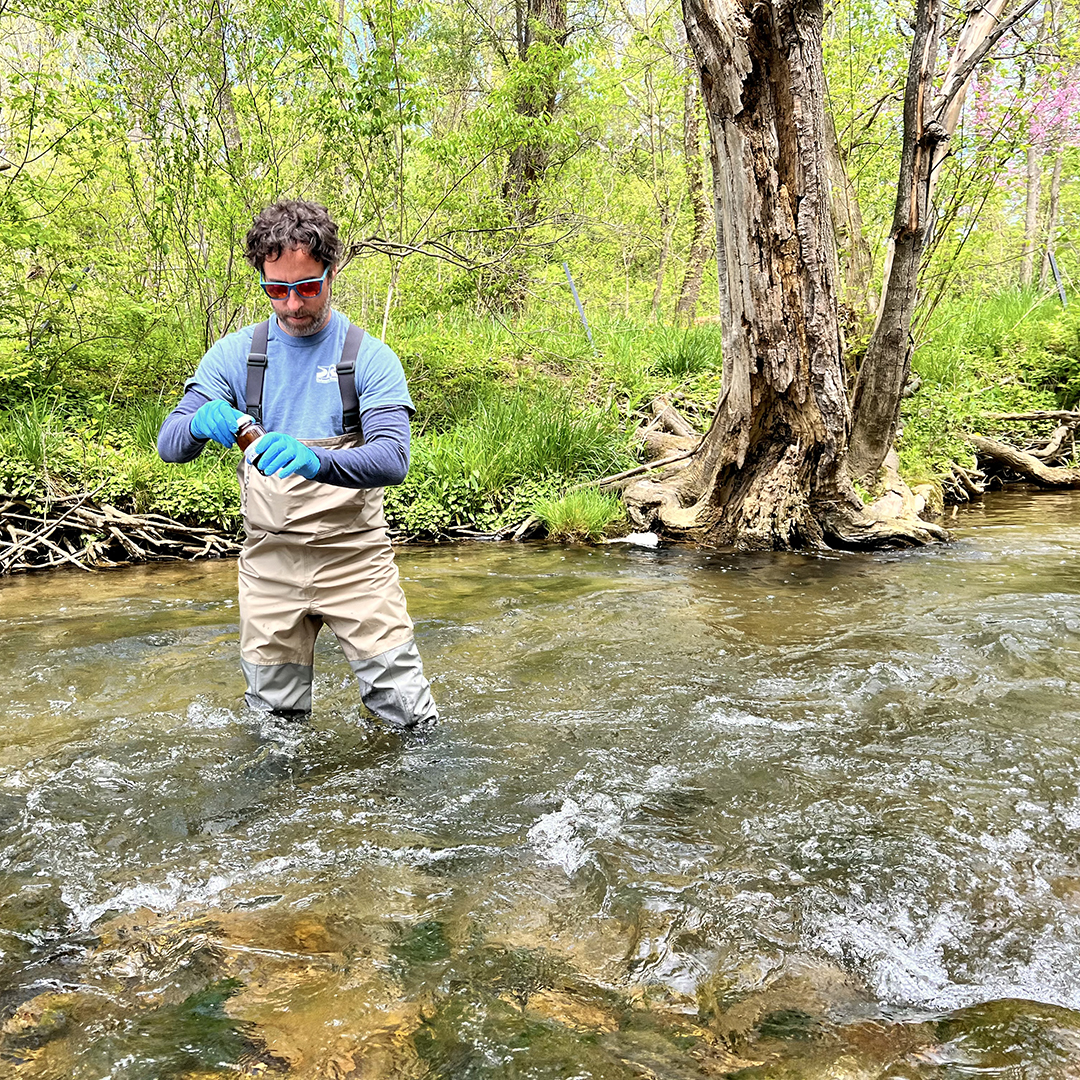 |
| DRBC staff collects a water sample from Valley Creek to monitor for 6PPD-Q. Photo by the DRBC. |
What is 6PPD-Q?
All tires have a chemical called 6PPD that keeps them from cracking and extends the life of tires. Through driving, tiny bits of rubber tire particles containing 6PPD are shed onto driving surfaces. Roughly 10% of these particles enter waterways via stormwater runoff (rain, wind), where 6PPD reacts with water to form 6PPD quinone (6PPD-Q). 6PPD can also leach off of tires submerged in water to form 6PPD-Q.
This could be a ubiquitous microplastic entering surface water systems in developed areas, making 6PPD-Q a contaminant of emerging concern.
6PPD-Q is acutely toxic to coho salmon and linked to die-off events in the Pacific Northwest. It is also sub-lethally toxic to other salmonid species, including rainbow, brown and brook trout, all species found in the Delaware River Basin.
DRBC Study
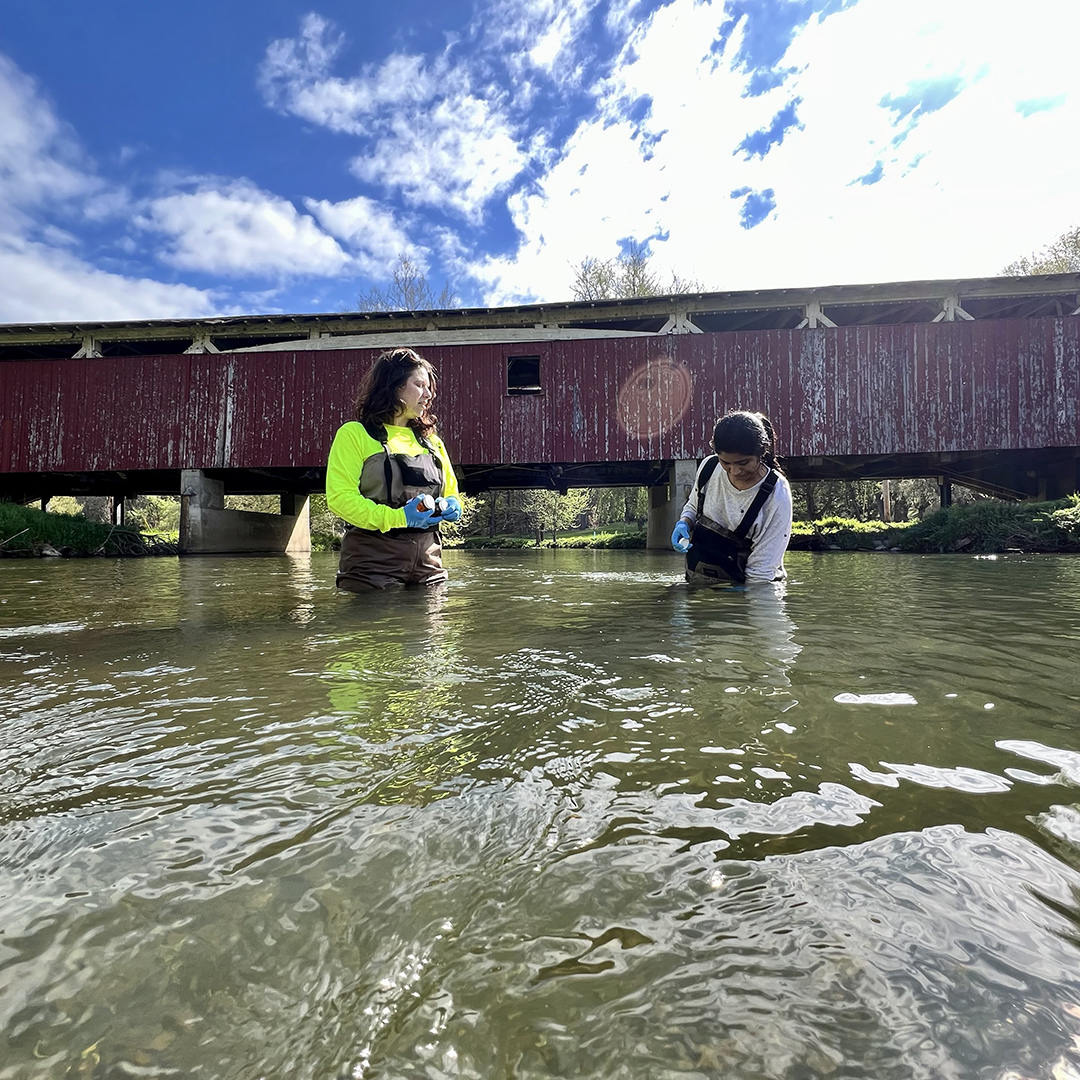
In 2023, the DRBC received grant funding from the National Fish & Wildlife Foundation to perform a first-of-its-kind study in the Delaware River Basin to determine if 6PPD-Q is present in Delaware River Basin waters under normal and/or stormwater flows.
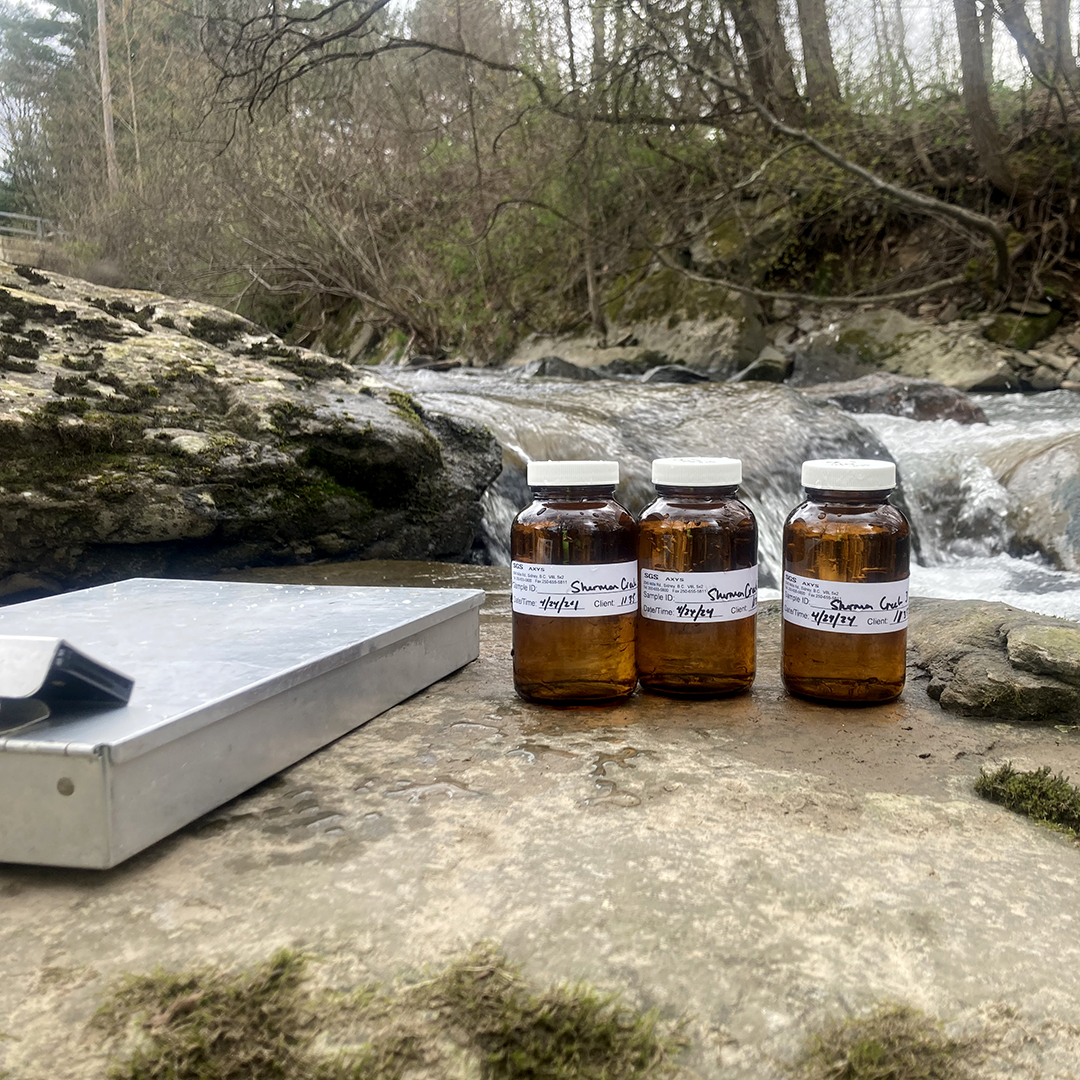
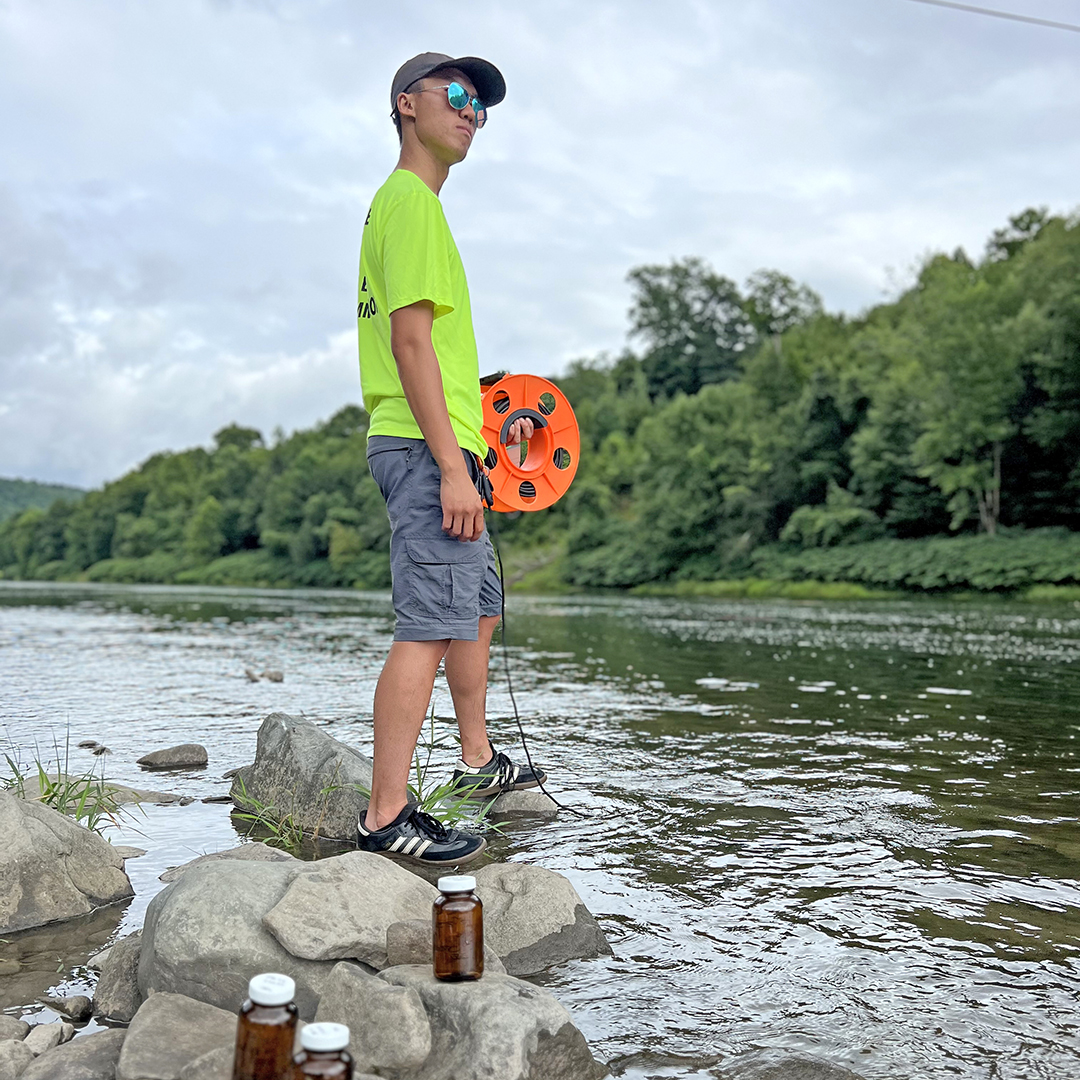
The study, which was funded from April 2024 through 2025, involved collecting water samples to develop baseline concentrations of 6PPD-Q in trout streams. Sampling continued quarterly for one year, with up to 3 additional sample collections after rain events to look at how heavy rainfall affects contaminant concentrations. Basic water chemistry (for example, pH, dissolved oxygen) was assessed as part of each sampling event.
Initial monitoring sites were selected based on their proximity to paved surfaces and reputation as high-quality trout streams.
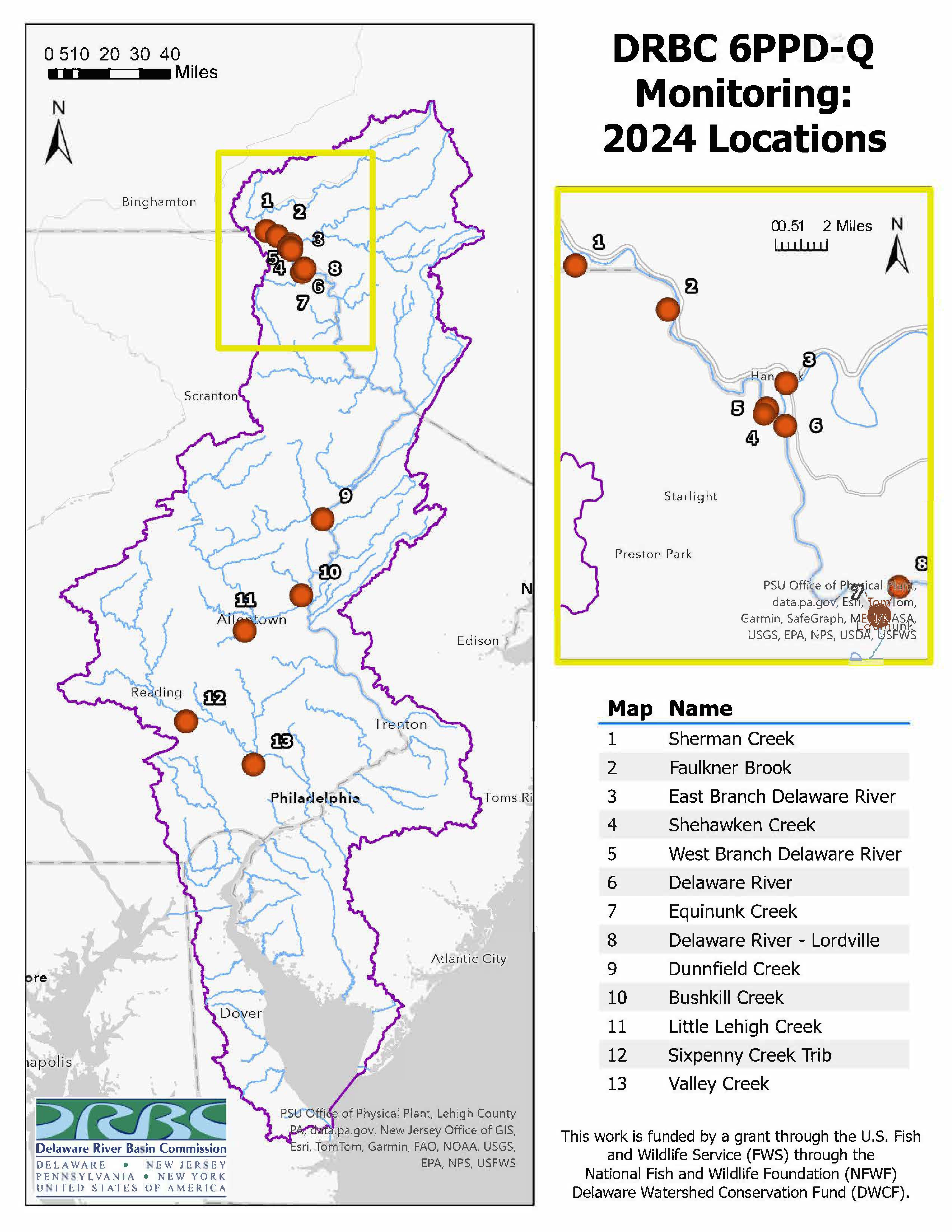 |
| Map of 6PPD-Q Sampling Locations (view as pdf) |
Sampling Locations
• Upper Basin: East Branch Delaware River, West Branch Delaware River, Sherman Creek, Faulkner Brook, Shehawken Creek, Delaware River at Hancock, Delaware River at Lordville and Equinunk Creek
• Middle Basin: Dunnfield Creek
• Lower Basin: Bushkill Creek
• Lehigh Basin: Little Lehigh Creek
• Schuylkill Basin: Sixpenny Creek, Valley Creek and a tributary to Valley Creek (when conditions allow)
Additional Monitoring of the Delaware River Mainstem
- From May 2024 through August 2024, 6PPD-Q monitoring was added to the Delaware Estuary Water Quality Monitoring Program at 8 sites from Eddystone up to Biles Channel.
Data to Date
- 6PPD-Q was found at every site sampled. Concentrations varied, but nearly all samples were well below known acute toxicity thresholds.
- We still have a lot to learn, especially about sub-lethal toxicity thresholds.
- Highest concentrations of 6PPD-Q are associated with stormwater runoff events, especially in the lower basin and near heavily traveled roadways.
Looking Ahead
- This work will contribute to the development of science-based, comprehensive strategies that identify, characterize and evaluate 6PPD-Q in DRB waters.
- DRBC plans to study additional streams using a USGS tool that scores watersheds based on 6PPD-Q threat.
Info on DRBC's Study
- It's Everywhere, but is it Toxic? A Basin-Wide Survey of 6PPD-Q in Brook Trout waters of the Delaware River Basin (poster by DRBC staff, SETAC 2025 North America Annual Meeting, November 2025; pdf)
- It's Everywhere, but is it Toxic? A Basin-Wide Survey of 6PPD-Q in Brook Trout Waters of the Delaware River Basin (presentation by DRBC staff, FUDR River Rendezvous; October 2025; pdf)
- Water Cooler Talk: PFAS & 6PPD-Q in the Delaware River Basin (presentation by DRBC Staff; Penn State Extension Webinar; August 2025; pdf)
- DRBC Brochure on 6PPD-Q (pdf)
- Trout and Toxics in the Upper Delaware Basin: Understanding a contaminant of emerging concern (presentation by DRBC staff, FUDR River Rendezvous; October 2024; pdf)
- "DRBC to study chemical from rubber tire particles as source of water contamination" (by Lauren Yates, Delaware Currents; February 2024)
American Chemical Society
Interstate Technology Regulatory Council
Society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry
- Acute Toxicity Testing of the Tire Rubber–Derived Chemical 6PPD-quinone on Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) and Brown Trout (Salmo trutta) (Anders Foldvik, Fedor Kryuchkov, Roar Sandodden, Silvio Uhlig; September 2022)
U.S. EPA
U.S. Geological Society
Copyright © Delaware River Basin Commission,
P.O. Box 7360, West Trenton, NJ 08628-0360
Phone (609)883-9500; Fax (609)883-9522
Thanks to NJ for hosting the DRBC website


